COVID-19 ELISA
pan-Ig Antibody Test
COVID-19 ELISA pan-Ig Antibody Test
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the University of Arizona partnered with the State of Arizona to provide COVID-19 Antibody Tests developed by AZClinCore to the general public.
In collaboration with UofA researchers Deepta Bhattacharya, PhD, Janko Nikolich-Žugich, MD, PhD, Bonnie LaFleur, PhD, and Andrew P Capaldi, PhD, AZClinCore completed clinical validation of the COVID-19 ELISA pan-Ig Antibody Test on 26 April 2020 and immediately applied for Pre-Emergency Use Authorization (Pre-EUA) to the U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Official Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) was granted on 31 August 2020 by the FDA (EUA201116).
The COVID-19 ELISA pan-Ig Antibody Test measures antibody responses (immune responses) and determines seroconversion intended for the qualitative detection of human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) antibody in human serum using two enzyme-linked immunoassays (ELISA). The test first targets the SARS-CoV-2 Spike receptor binding domain protein (RBD) and then positive samples are confirmed with a second assay targeting the Spike S2 Protein. The combinatorial use of spike RBD and S2 eliminates almost all false positives and can detect durable antibody production for at least 5-7 months after infection.
Over the course of the service, the lab continually updated the test with additional clinical validation studies as more information about the SARS-CoV-2 virus became available. In February 2021 AZClinCore implemented new assay threshold/cut-off values based on re-analysis with asymptomatic patients. In April 2021, AZClinCore reevaluated the test’s predictive value using 427 vaccinated individuals; along with the previously analyzed symptomatic and asymptomatic presumed positive individuals in the study, this resulted in a sensitivity of 96% and a specificity of 98%. From 29 April 2020 to 22 September 2021, AZClinCore provided 44,524 test results to Arizona residents.
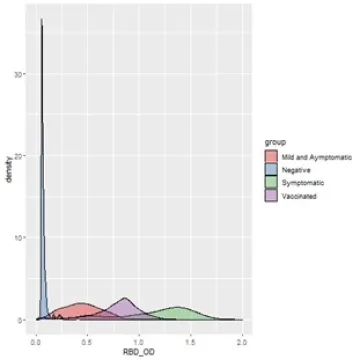
Distribution of OD values for negative, asymptomatic, symptomatic and vaccinated individuals for RBD assay:
Although AZClinCore revoked its EUA on 16 December 2022 after demand for clinical testing waned, AZClinCore continues to run the assay in a research capacity and has developed a multitude of related research assays including variant-specific quantitative titer and surrogate neutralization assays for a large scale study with the CDC, facilitated by UofA researcher Jeff Burgess MD, MS, MPH. With its high-throughput capabilities facilitated with an array of Beckman liquid-handling robots and highly trained clinical technologists, AZClinCore has the capacity to process 5,120 qualitative reactions and 768 quantitative titer reactions per day. For this study, AZClinCore has processed over 45,000 total samples and has run over 375,000 total reactions.
See: Inside an Antibody Testing Laboratory
Resulting Publications
Herring, M.K., J.K. Romine, M.G. Wesley et al. 2022. SARS-CoV-2 infection history and antibody response to three COVID-19 mRNA vaccine doses. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2022; ciac976, doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac976
Jergović, M., J.L. Uhrlaub, M. Watanabe et al. 2022. Competent immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 variants in older adults following mRNA vaccination. Nature Communications 13, 2891 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30617-9
Ripperger, T.J., J.L Uhrlaub, M. Watanabe, et al. 2020. Orthogonal SARS-CoV-2 Serological Assays Enable Surveillance of Low-Prevalence Communities and Reveal Durable Humoral Immunity. Immunity. 2020 Nov 17; 53(5): 925–933.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.004
COVID Antibody
COVID-19: University of Arizona Antibody Testing Process
CLINICAL UTILITY
This serological test for SARS-CoV-2 exposure quantifies antibodies reactive to the S2 and receptor binding domain (RBD) of spike protein using Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA). SARS-CoV2 causes infections of the respiratory tract, triggering an immune response and antibody production directed towards viral antigens within 1-2 weeks of exposure and symptom onset. Such antibodies can be detected in the serum and plasma of subjects with ongoing infections and those with prior exposures.
Antibody tests have not been shown to definitively diagnose or exclude SARS-CoV-2 infection. Positive results could also be due to past or present infection with non-SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus strains, such as coronavirus HKU1, NL63, OC43 or 229E. Diagnosis of COVID-19 is made by detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by molecular testing methods, consistent with a patient’s history, clinical observations and epidemiological information.
Criteria for Patient Testing
- For prescription use only
- For in vitro diagnostic use only
Specimen Requirements
SAMPLE TYPE: Serum
VOLUME: 1.0 mL of serum from adult patients and 0.5 mL of serum from pediatric patients
CONTAINER: Whole blood collected in red-top (no anticoagulant) or gold-top/tiger-top serum separator tube (SST)
Acceptable Specimens
Serum should be separated from specimen within 90 minutes after collection. Note: Tube should be at room temperature before centrifugation
UNACCEPTABLE SPECIMENS: Specimens which are severely lipemic and/or hemolyzed are not acceptable
Specimen Storage
Serum separated from whole blood, either by gel/SST or manual transfer, is stable for:
- up to 3 days at room temperature
- up to 1 week when refrigerated at 2–8°C
- up to 6 months when frozen (-20°C or lower)
TRANSPORT TO THE LABORATORY: Specimens should be delivered to the AZClinCore location as soon as possible. If transport is delayed, serum separated specimens should be refrigerated (2–8°C)
Turnaround Time
Results returned 5–10 days from receipt of the specimen by AZClinCore, based on business hours of the laboratory: Monday through Friday, 9am–5pm Arizona Time.
PURPOSE OR PRINCIPLE
Qualitative detection of total antibodies to human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in human serum to aid in identifying individuals with an adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2, indicating recent or prior infection.
Methodology and Additional Details
The assay is an ELISA-based test utilizing a polystyrene testing plate containing sample wells comprised of a hydrophilic high binding surface that binds and immobilizes polar proteins and peptides. The assay begins by binding the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to the testing plate (in the separate confirmation assay the RBD protein is replaced by the SARS-CoV-2 S2 protein, all subsequent steps are identical). Once the target protein is bound to the plate the patient serum is added. Any patient antibodies specific to the SARS-CoV-2 virus are then bound to the target protein and all other antibodies are washed away. An anti-human Ig secondary antibody is then added and used to bind to the previously bound serum antibodies and is conjugated with a horseradish peroxidase enzyme. In the next step 3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) is added to the reaction as a chromogenic substrate that undergoes oxidation in the presence of peroxidase enzymes and generates a blue color that can be read at 630nm wavelengths. Finally, a 2N sulfuric acid solution is added to the reaction to quench the TMB and act as a stop reagent. This causes the reaction to generate a yellow color which can be read at 450nm wavelengths. The reaction is then read using a fluorometric plate reader to record the optical density of the reaction at both 630nm and 450nm wavelengths. Any signal above baseline in the 630nm wavelength is treated as having incomplete quenching and the sample is queued for re-run. Optical densities at 450nm wavelengths are recorded and reported as raw data for patient samples.
Interpretation
Qualitative results for the detection of SARS-CoV2-specific antibodies are reported as POSITIVE or NEGATIVE.
Positive results are indicative of either active or prior infection with SARS-CoV2, or an immune response resulting from vaccination. It is yet undetermined what level of antibody to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein correlates to immunity against developing symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 disease. Antibody tests have not been shown to definitively diagnose or exclude SARS-CoV-2 infection. Positive results could also be due to past or present infection with non-SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus strains, such as coronavirus HKU1, NL63, OC43 or 229E. Diagnosis of COVID-19 is made by detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by molecular testing methods, consistent with a patient’s history, clinical observations and epidemiological information.
Negative results do not rule out SARS-CoV-2 exposure; it usually takes at least 10 days after symptom onset for antibody response to reach detectable levels. False negative results can sometimes occur. This can happen if you get an antibody test too soon after being exposed or vaccinated and your body has not yet made enough antibodies to be detected by the test. Additionally, some individuals, such as those with weakened immune systems due to a medical condition or certain medications, may not develop detectable levels of antibodies after exposure or vaccination. If you are concerned about your results, it is important to follow up with a healthcare provider, who can evaluate your medical history.
Limit of Detection
Do not test samples collected prior to 14 days from symptom onset, Covid diagnosis or vaccination with the COVID-19 ELISA pan-Ig Antibody Test because there is an increased risk of false negative results. In patients tested 14 days or greater from diagnosis or vaccination, the sensitivity of the COVID-19 ELISA pan-Ig Antibody Test is 96.20% and specificity is 97.81%.
FDA Comments
This test was developed and its analytical performance characteristics have been determined by the Arizona Molecular Clinical Core (formerly the University of Arizona Genetics Core for Clinical Services). It has not been cleared or approved by FDA. This assay was developed as a Laboratory-Developed Test and has been validated pursuant to the CLIA regulations and is used for clinical purposes. This test has been authorized by FDA for use by Arizona Molecular Clinical Core. This test is only authorized for the duration of the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of emergency use of in vitro diagnostic tests for detection and/or diagnosis of COVID-19 under Section 564(b)(1) of the Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b)(1), unless the authorization is terminated or revoked sooner. (REVOKED 16 December 2022)
| CALL US | EMAIL US | VISIT US |
|---|---|---|
| Call Center (520) 626-5002 Fax (520) 626-7701 |
Contact Us - online form AZClinCore@arizona.edu |
Arizona Molecular Clinical Core |


Copyright © 2023 Arizona Molecular Clinical Core All Rights Reserved
